HAUG Charging Triodes Power Supply Is From TR 150 Charging Generator
 HAUG charging triodes are characterized by a very homogenous field around the charging pins. Due to the special geometry of the charging triode, no spark-over to the counter-electrode can occur. The charging triode can therefore be mounted at a distance of approx. 10–30 mm from the material to be charged. The supply to the charging triodes is from the charging generator TR 150 which is available with either positive or negative polarity.
HAUG charging triodes are characterized by a very homogenous field around the charging pins. Due to the special geometry of the charging triode, no spark-over to the counter-electrode can occur. The charging triode can therefore be mounted at a distance of approx. 10–30 mm from the material to be charged. The supply to the charging triodes is from the charging generator TR 150 which is available with either positive or negative polarity.
The direct voltage output of the charging generator can be set steplessly, and a remote option is also available. The charging triode ensures a high charging performance even with very low direct voltage outputs and therefore ensures very good fixation. Due to their simple design incorporating magnetic clamps, the charging pins can be replaced very easily when worn. The charging triode is connected by means of a shielded high-voltage cable with plug-and-socket connector.
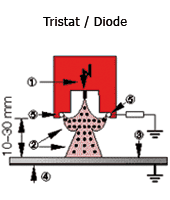 |
1. Positive or negative voltage |  |
| 2. Electrical field | ||
| 3. Insulator (e.g. film) | ||
| 4. Counter-electrode (e.g. grounded metal plate) |
||
| 5. Intake electrodes |
HAUG-Charging Systems
HAUG charging systems are designed to apply electrostatic charges without physical contact. These systems can be used for any application where different materials are to be pinned together electrostatically. At least, one of these materials must be non-conductive. The electrostatic pinning serves to enhance subsequent processes, such as film/foil overlapping in packaging machines.
Electrostatic charges are applied using charging bars, electrodes or triodes which are supplied with positive or negative high-voltage from a steplessly adjustable charging generator. In order to charge two-dimensional or partial areas, bar-shaped electrodes or triodes are used. A resistance-coupled version for special requirements is also available.
Applications
HAUG charging systems can be used, among others, in the following applications:
- for fixing and positioning films and foils, paper and cardboard, e.g. on steel sheets, glass panels, wood panels or similar;
- in the production of CDs to reinforce adhesion
- for blocking film and paper stacks
- for IML technology
In order to ensure a continuous, reliable charging process, we strongly recommend discharging the materials to be bonded to each other using a suitable HAUG ionization system before charging.
Technical Data
| Dimensions | approx. 270 x 170 x 150 mm (B x H x T) |
| Protection Type | IP 30 |
| Protection class | I |
| Supply voltage | 115 VAC / 230 VAC (50 – 60 Hz) |
| HV-terminals | 1 (AG) |
| Power consumption | 30 VA |
| Output voltage | Umax = 15 kV ± 10% |
| Output voltage | (lmax) = 300 µA ± 15% |
| Signaling contacts monitoring | Contact rating max. 24 VAC / 35 VDC, max. 50 mA |
| Pulse frequency via pulse input | max. 1 Hz (max. 106 Zyklen) |
| Recovery time after overload switch-off | < 10 s |
| Operating temperature | +5 °C to +45 °C |
| Storage/transport temperature | -15 °C to +60 °C |
| Weight | 7 kg |
| Mains cable | 2,6 m; fixed to the device |
Subject to technical changes!
Variants
| Digital display |
Overcurrent | Remote control | Pulsing | Reset | Monitor- output |
|
| A | voltage and current |
switch-off | none | floating normally open contact |
floating normally open contact |
0 – 10 V |
| S | none | switch-off | 0 – 10 V | 24 VDC | 24 VDC | 0 – 10 V |
| P | none | switch-off | 4 – 20 mA | floating normally open contact |
floating normally open contact |
4 – 20 mA |
HAUG Static Control Products And Solutions For Industry

